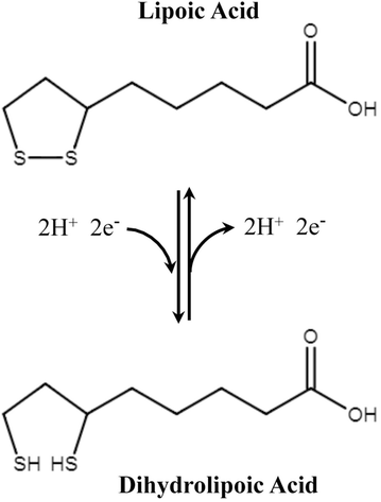
Free-radical Scavengers
Antioxidants are substances that can prevent or slow damage to cells caused by free radicals, unstable molecules that the body produces as a reaction to environmental and other pressures.
Free radicals are highly unstable molecules that are naturally formed when you exercise and when your body converts food into energy.
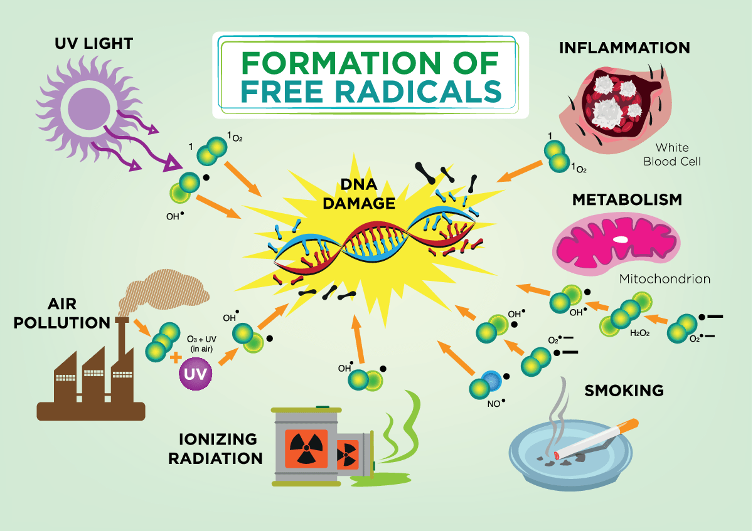
Factors that increase the production of free radicals in the body can be internal, such as inflammation, or external, for example, pollution, UV exposure, and cigarette smoke.
Antioxidants Benefits
Antioxidants can protect against the cell damage that free radicals cause, known as oxidative stress.
Activities and processes that can lead to oxidative stress include:
- mitochondrial activity
- excessive exercise
- tissue trauma, due to inflammation and injury
- ischemia and reperfusion damage
- consumption of certain foods, especially refined and processed foods, trans fats, artificial sweeteners, and certain dyes and additives
- smoking
- environmental pollution
- radiation
- exposure to chemicals, such as pesticides and drugs, including chemotherapy
- industrial solvents
- ozone
Such activities and exposures can result in cell damage.
This, will lead to:
- an excessive release of free iron or copperions
- an activation of phagocytes, a type of white blood cell with a role in fighting infection
- an increase in enzymes that generate free radicals
- a disruption of electron transport chains
All these can result in Oxidative Stress.
The damage caused by oxidative stress has been linked to cancer, atherosclerosis, and vision loss. It is thought that the free radicals cause changes in the cells that lead to these and possibly other conditions.

An intake of antioxidants is believed to reduce these risks.
According to one study : “ Antioxidants act as radical scavenger, hydrogen donor, electron donor, peroxide decomposer, singlet oxygen quencher, enzyme inhibitor, synergist, and metal-chelating agents .”
Other research has indicated that antioxidant supplements may help reduce vision loss due to age-related macular degeneration in older people.
Free Radicals, Antioxidants in Disease and Health
Int J Biomed Sci . 2008 Jun; 4(2): 89–96 Lien Ai Pham-Huy , Hua He ,and Chuong Pham-Huy .
Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39:44–84,Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M.
Importance of iron chelation in free radical-induced oxidative stress and human disease
Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17:3460–73,Jomova K, Valko M.
How can antioxidants benefit our health
Medical News Today, May 29, 2018, Megan Ware, RDN, L.D. Medically reviewed by Natalie Olsen, R.D., L.D., ACSM EP-C .
Antioxidants in health and disease
J Clin Pathol. 2001;54:176–86,Young IS, Woodside JV.
The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/
/nitrosative stress
Nutrition Journal volume 15, Article number: 71 (2015),Ergul Belge Kurutas